Preparations for stimulating ovulation. Injections and pills to help get pregnant.
To get pregnant, you need to fulfill three basic conditions:
- the woman has ovulated;
- the sperm has fertilized the egg;
- the fetus is firmly fixed in the uterus.
Respectively:
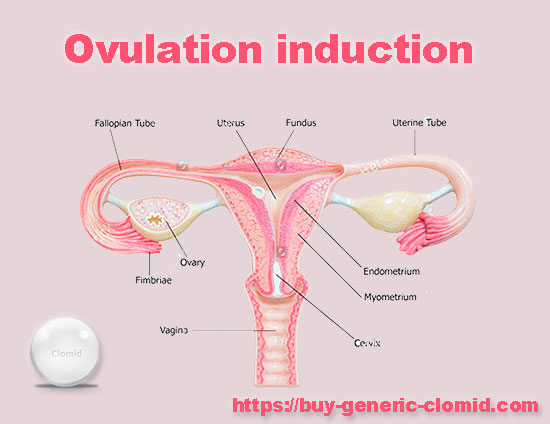
- drugs that enhance the production of FSH and LH, which help to get pregnant, stimulate ovulation – the growth of follicles on the ovaries;
- HCG helps the largest follicle to stay big enough to release an egg for a sperm to fertilize;
- progesterone prepares the inner layer of the uterus to secure the embryo and helps to carry the fetus.
Who needs preparations for stimulating ovulation
If the question “Why can’t I get pregnant?” is relevant for you, then you need to undergo an examination. Well, if your spouse does the same, it would help to establish the cause of infertility.
Ovulation stimulation should be recommended by a doctor after a series of examinations that will give accurate data on the cause of problems with independent conception. The doctor prescribes drugs to stimulate ovulation in cases where:
- The patient noted a rare maturation of the egg and its release from the ovaries;
- The couple has been trying to conceive for over a year to no avail;
- Spouses older than 35-40 do not get pregnant within 6 months.
In this case, stimulation of ovulation is prohibited in the following cases:
- Partner infertility
- The presence of inflammation of the appendages, with andexitis
- With pathologies of the uterus
- In case of poor patency of the fallopian tubes
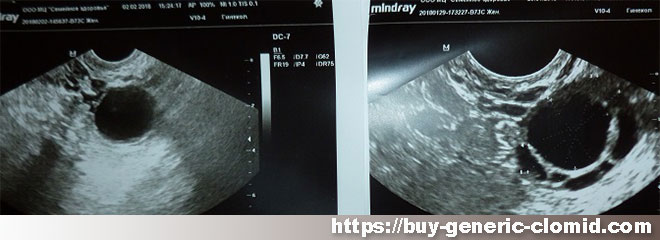
Drugs that help get pregnant, such as Clomid, are selected individually, depending on the results of tests and ultrasound examinations.
Frequently Asked Questions Related to Getting Pregnant
Can I get pregnant with PCOS?
The chance of getting pregnant with PCOS is very low. The greater the number and size of cysts, the less chance of conceiving a child.
Can I get pregnant with uterine fibroids?
The presence of fibroids significantly reduces the likelihood of pregnancy. The larger the diameter of the nodes, the less chance of pregnancy.
Can I get pregnant with endometriosis?
The probability of conceiving a baby with a diagnosis of endometriosis is, but very small. Severe stages of endometriosis can cause infertility.
Will I be able to get pregnant in the future if my first pregnancy ended in an abortion?
Doctors do not recommend ending the first pregnancy with a surgical abortion – the likelihood of infertility in this case is high. However, this is not the rule: some women safely bear children even after several abortions.
How to use prescribed preparations for stimulating ovulation
Drug regimens depend on the stimulation protocol, so you must strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations. Most drugs are administered intramuscularly or subcutaneously. Many of them have their own characteristics regarding the use and storage, and they are associated not only with the drug itself, but also with the form of release proposed by the manufacturer. In this regard, we advise you to make the first injection in our treatment room, where the nurse will tell you, and most importantly, show you how to properly administer a particular drug. We categorically do not recommend making injections according to the description on the Internet – the price of an error may be too high.