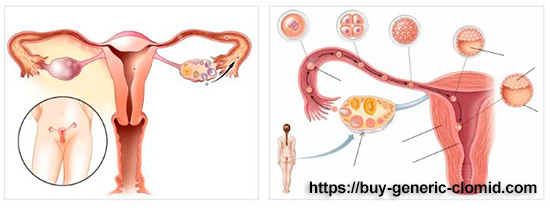
Increasingly, women are turning to a gynecologist with problems with conception. But medicine does not stand still, it is constantly developing, so the desired pregnancy can occur after treatment with special drugs that stimulate ovulation.
Reasons for lack of ovulation
Most often, the inability to get pregnant is associated with the lack of ovulation as such or with its incorrect course. There may be several reasons for this:
- Diseases of the pelvic organs of an infectious and inflammatory nature (chronic salpingoophoritis, polycystic ovaries, cysts, etc.).
- Too small a woman’s weight is usually less than 48 kg, in which there is insufficient production of sex hormones, which leads to a lack of ovulation and amenorrhea.
- Hormonal changes in the body against the background of stress, excessive weight (when the body mass index is more than 25), certain diseases of the thyroid gland (Hypo – or hyperthyroidism), etc.
- Long-term use of oral contraceptives. In this case, the body stops producing hormones on its own, and it sometimes takes several months to fully restore this ability.
- Excessive physical activity can also negatively affect ovulation, especially if it is associated with taking synthetic sports nutrition supplements. These drugs have a very negative effect on the female reproductive system.
In what cases do I need stimulation and when it is not carried out
Ovulation stimulation is possible when a couple cannot conceive a child for a year. If the age of a woman is 35+, this period can be reduced to six months. In any case, a thorough diagnosis (preferably of both partners) is necessary to identify the true causes of infertility and make a decision about stimulation. In particular, the following diagnostic tests are carried out:

- Collection of the patient’s medical history, which takes into account her age, the presence/absence of abortions and pregnancies, miscarriages, chronic diseases, carrying an intrauterine device, etc.
- The patency of the fallopian tubes is checked. Non-operative and operative methods are used for this purpose. The first include metrosalpingography (x-ray examination). A variation is ultrasonic metrosalpingography, when using a contrast agent and ultrasound equipment to check the patency of pipes. These methods are not universal and have their disadvantages, such as the harmfulness of radiation and possible errors in the result. For more accurate diagnostics, laparoscopy is used-an operative study, but it gives the most reliable results.
- The usual ultrasound examination, which can show possible inflammatory processes, polycystic, various neoplasms and other pathologies of the female reproductive system.
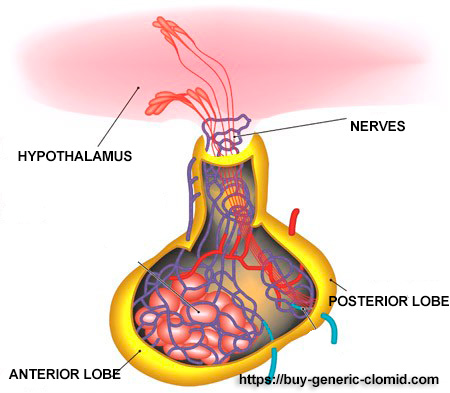
- In some cases, ovulatory failures may occur due to hormonal disorders, so it is mandatory to donate blood to determine the amount of female sex hormones. At the same time, it is recommended to conduct research on the activity of the thyroid gland, since this organ has a direct impact on female fertility.
- The partner’s spermogram should also be performed, since sometimes the reason for the absence of pregnancy can be insufficient mobility and viability of spermatozoa.
- Test the compatibility of the partners. If the results are unfavorable, the doctor may suggest artificial insemination.
It should be noted that contraindications to stimulation are inflammatory diseases of the uterus and (or) ovaries, tubes, adjacent organs and systems (urinary tract, gastrointestinal tract), hormonal fluctuations, the onset of menopause or pre-climatic period.
After diagnostic measures and in the absence of absolute contraindications, the gynecologist decides to prescribe drugs that stimulate ovulation.
Methods of ovulation stimulation
Ovulation stimulation is impossible without taking vitamin complexes and useful trace elements. True female” vitamins include E, A, B (folic acid is required), and C. additionally, vitamin D is recommended, especially for women living in areas where Sunny days are rare.
Vitamin A helps follicle maturation and regulates the amount of cervical fluid. B vitamins are recommended to be taken both at the planning stage of pregnancy and during it, as they not only prolong the luteal phase of the cycle, promote endometrial growth and egg maturation, but also during pregnancy eliminate toxicosis, prevent miscarriages and help healthy fetal development. Vitamin E stimulates the maturation of the yellow body, “supports” ovulation itself and increases the production of progesterone, which is especially useful when this hormone is insufficient. Vitamin C helps normalize the hormonal background, and also serves as a means to prevent the development of DNA abnormalities in the future fetus. Also, when preparing for pregnancy, it is advisable to monitor the sufficient intake of polyunsaturated omega-3 fatty acids in the body. They are most concentrated in oily fish, synthetic fish oil, and Flaxseed and olive oils. Drugs containing selenium, zinc, and iron are also used to stimulate ovulation.
All these methods of restoring ovulatory function are effective. However, you can’t use them at random. A doctor’s consultation is necessary, as well as an extensive and comprehensive diagnosis of both partners.