Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome is characterized by an increase in the ovaries with the development of numerous cysts (the condition of polycystic ovaries), the accumulation of fluid in the tissues, abdominal cavity and lungs. In 2% of cases, this condition requires immediate hospitalization. The occurrence of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome is associated with a sharp rise in the level of estrogens (estradiol) under the influence of gonadotropins, which can lead to the rapid development of ovarian cysts.
This disease occurs in 10-20% of cases after ovulation induction, mainly mild and moderate severity. With a mild degree of this syndrome, the ovaries are enlarged to 5 cm in diameter, there is also a slight ascites and weight gain of up to 5 kg. With moderate severity of the syndrome, the ovaries are enlarged from 5 to 12 cm, there is moderate ascites, nausea, vomiting, discomfort in the lower abdomen, and an increase in body weight of more than 5 kg. Severe cases of ovarian hyperstimulation are characterized by an increase in the ovaries, severe ascites, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, shortness of breath, accumulation of fluid in the lungs, dropsy, blood thickening, and can lead to kidney failure.
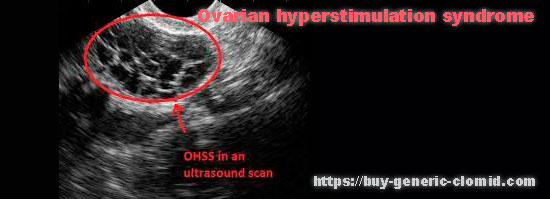
Severe forms occur in young women with irregular rare menstruation, who after the first induction had a condition of polycystic ovaries (more than 15 follicles). Hyperstimulated ovarian syndrome has two phases. The first phase manifests itself from the second to the seventh day after ovulation, and the number of signs of the disease is limited. The second phase occurs after a woman becomes pregnant.
How is hyperstimulated ovarian syndrome treated?
Women with mild to moderate syndrome can stay at home, preferably in bed, strictly controlling the amount of fluid consumed and excreted. If, after the induction of ovulation, a woman has dramatically recovered by 1-1.5 kg, it is advisable to hospitalize such a woman. Severe cases should be treated in hospital conditions, taking into account the condition of the woman.
Prevention
When conducting ovulation induction, it is very important to monitor the reaction of the ovaries to the administration of medications, which can be done using ultrasound. If there is a development of 1-3 follicles up to 18-20 mm in size, such induction can be considered safe. However, with the appearance of 5 follicles or more, as well as with a sharp increase in blood estradiol, it is advisable to stop the induction of ovulation.