Poor nutrition is one of the reasons why some women can not get pregnant. Such conclusions were made by scientists on the basis of large-scale studies conducted. On their basis, a fertile diet was compiled, designed to increase the ability to conceive a baby.
The fact that the use of a certain set of products helps to get pregnant (we also remind you that clomid copes with this task perfectly) became known in the early 90s. Scientists have developed a special nutrition system after a long eight-year study in which more than 18 thousand women took part. The diet, called fertile, increases the chances of getting pregnant, and also affects the development of the fetus.
By the way, other studies conducted on animals have shown that a certain type of nutrition of parents before conception has a serious impact on the health of offspring.
Of course, when planning a pregnancy, you should not rely only on a diet, but as studies show, it can really increase the chances of conception. But of course, if a woman does not have serious problems like infection, clogged fallopian tubes, or if the cause of infertility is not any irreversible painful processes. What should be the nutrition of future parents?

What foods can not be consumed if you want to get pregnant
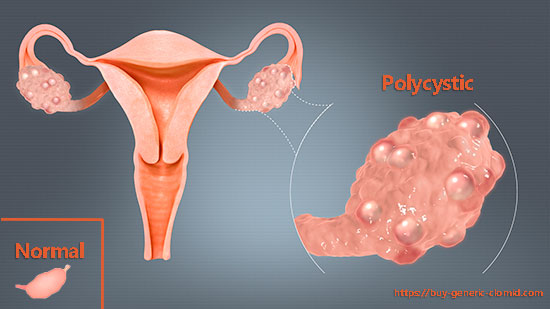
First of all, it is important to exclude from the diet coffee and products containing caffeine-Coca-Cola, Pepsi, etc. The fact is that caffeine suppresses the reproductive function of the body. Caffeine stimulates the production of androgens by the liver, adrenal glands, and ovaries. The increased amount of androgens does not have time to turn into sex hormones, as a result, the endocrine balance is disturbed. As a result, there is a lack of ovulation, an incompetent egg or sperm, polycystic ovary syndrome. Nicotine has the same effect.
You should also give up sugar and flour products. After consuming sugar and products with it, the glucose level increases. To reduce it, the body produces insulin, which can cause polycystic ovary syndrome, which is one of the most common causes of female infertility, problems with conception and even carrying a child.
Products with preservatives and dyes are also on the black list, since they directly affect the viability of the egg and sperm cells. In addition, settling in the liver, they disrupt its proper functioning, causing increased production of androgens.
Fertile diet: What does a woman have to get pregnant faster
The diet of the expectant mother should be rich in healthy fats, whole-grain products, vegetable proteins. All these products support the eggs in working condition, contribute to regular ovulation, normalization of sugar levels, and as a result, the onset of a long-awaited pregnancy.
Meat consumption should be reduced in favor of vegetable proteins – legumes, nuts, as well as fish and seafood. The researchers note that the use of excessive amounts of protein can negatively affect the attachment of the embryo to the uterine wall or interfere with its early development.
The diet should also contain a sufficient amount of vitamin E (vegetable oils).
As for dairy products, they should not be decontaminated. When following a fertile diet, it is recommended to consume fatty milk, cheese and yogurt. Dairy products with normal fat levels contribute to the production of a hormone associated with ovulation and fertility.
A distinctive feature of the fertile diet from others is the high level of folic acid. As is known, this acid plays a special role not only in conception, but also in the development of the embryo.
Fruits, nuts and greens are especially rich in folic acid.
Foods rich in vitamin C also contribute to the improvement of reproductive functions in women. In this regard, it is necessary to increase the consumption of citrus fruits, kiwis, apples, pears, wild berries, tomatoes, bell peppers and broccoli.
Experts recommend eating five servings of vegetables and fruits a day: three vegetables and two fruits. One fruit or vegetable is equal to one serving. It is also necessary to take vitamins.
These studies of the influence of nutrition on the probability of conception were conducted by scientists at the Harvard Medical Institute in Boston