One of the reasons for infertility in women is the lack of ovulation, when there is no exit from the follicle of a mature egg, which, in fact, should be fertilized by spermatozoa. This condition is called anovulation. What drugs for ovulation stimulation exist today?
Treatment of anovulation is carried out by stimulating ovulation, for which drugs aimed at activating ovarian function are used, the most popular of which are clomid, clomiphene citrate, pregnil and clostylbegit.
Clomid – drugs for ovulation stimulation
Other names of Clomid: Ardomon, Biogen, Blesifen, Clofert, Clomhexal, Clomifeencitraat cf, Clomifen, Clomifene, Clomifeno, Clomifenum, Clomifert, Clomipheni, Clomivid, Clomoval, Clostilbegyt, Clovul, Dufine, Duinum, Dyneric, Fensipros, Fermid, Fermil, Fertab, Fertil, Fertilan, Fertin, Fetrop, Genoclom, Genozym, Gonaphene, Gravosan, Ikaclomin, Indovar, Klomen, Klomifen, Kyliformon, Milophene, Ofertil, Omifin, Orifen, Ova-mit, Ovinum, Ovipreg, Ovofar, Ovuclon, Ovulet, Pergotime, Phenate, Pinfetil, Pioner, Profertil, Prolifen, Provula, Reomen, Serofene, Serpafar, Siphene, Spacromin, Tokormon, Zimaquin.
Initially, clomid was developed to treat such a serious disease as breast cancer. However, the drug was not widely used in this area of treatment, as it did not meet the inflated expectations. Later, it was used as a drug that helps stimulate ovulation for women who have problems with the onset of conception due to a violation of the ovulatory cycle. Clomid is prescribed in the following cases:
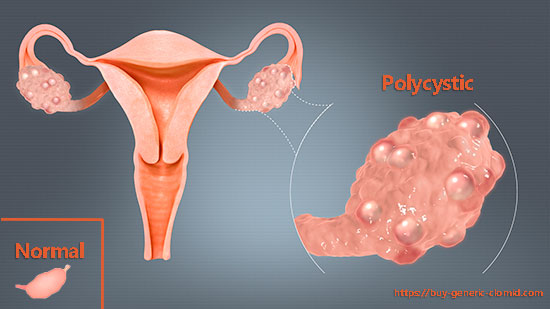
- if the development of anovulation occurred due to the presence of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS);
- with infertility of unclear genesis: if, from a medical point of view, a woman has no obstacles to the onset of conception, but pregnancy does not occur. It is recommended to supplement the use of clomid with metformin, which helps to increase insulin levels and stimulate ovulation;
- for additional guarantees during ovulation stimulation before in vitro fertilization (clomid increases the chances of a successful pregnancy).
The optimal course of use of this drug should be six months, unless, of course, pregnancy occurs earlier than this period, which happens in 30% of cases.
Clomid has minor side effects, in the process of taking it, painful sensations in the lower abdomen, sleep disturbance and weight gain can be observed. In extremely rare cases, taking clomid threatens the development of a cyst or ovarian tumor.
Pregnil
Pregnil is a drug based on human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). Its use is prescribed to women of any age, however, depending on various factors, clomid has different effects. The purpose of its use as a therapeutic agent in the treatment of infertility is to stimulate the activity of the ovaries as part of the artificial insemination program.
The highest concentration of hCG in a woman’s body is observed 20 hours after the first intake of the drug. The excess of the drug is excreted from the body independently after a few days.
Clomiphene Citrate
Clomiphene citrate is not very popular among medical professionals due to its notoriety associated with the side effects of the drug. Against the background of taking clomiphencitrate, the size of the ovaries may increase, urination becomes more frequent, visual function is impaired, and vasomotor symptoms often occur. However, clomiphene citrate is indispensable in cases where there is no possibility of folliculometry. Clomiphene citrate has contraindications: it cannot be used for ovarian cysts.
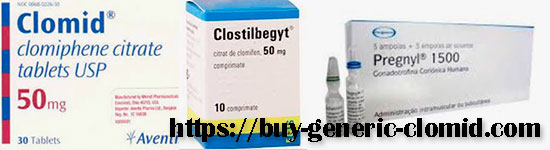
Drugs for ovulation stimulation: Clostylbegit
Clostylbegit is rightfully considered one of the most popular drugs that promote ovulation stimulation. Its effectiveness especially increases against the background of taking other drugs with a similar effect. Clostylbegit increases the level of FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone) in the female body, provided that medications are taken simultaneously to reduce prolactin levels during ovulation stimulation, which ensures its effectiveness.
The dosage of clostylbegit should be calculated by a doctor in accordance with the patient’s medical indicators and the individual characteristics of her body. The absence of ovulation after several courses of taking the drug may signal the presence of certain pathologies of the reproductive system. A side effect of clostylbegitis may consist in thickening of cervical mucus, which prevents the movement of spermatozoa.