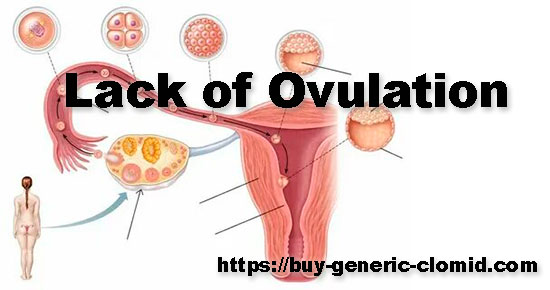
Anovulatory cycle – how to wake up sleeping eggs. In the ovary there are special structures – follicles in which eggs mature. In the middle of the cycle, the follicle ruptures, releasing the mature germ cell into the fallopian tube to meet the sperm. However, in some cases, the egg does not leave its container and does not seek to fertilize.
Cycles that are not accompanied by ovulation are called anovulatory. Such a violation leads to infertility.
How the female body works and why nature fails
Normally , the menstrual cycle is divided into three phases:
- Follicular, occurring after the end of menstrual bleeding. During it, the cerebral appendage – the pituitary gland – secretes follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which “spurs” the development of follicles, one or two of which will burst in the middle of the cycle and release mature eggs. In parallel, the ovaries increase the production of female hormones-estrogens, especially estradiol.
- Ovulatory – closer to the end of egg maturation, the production of another hormone – luteinizing (LH) begins. Under its influence, ovulation occurs. The follicle bursts, and the egg goes into the fallopian tube to meet the sperm.
- The phase of the corpus luteum, during which the fertilized cell descends into the uterus and is implanted. The burst follicle turns into a yellow body, secretes progesterone and sex hormones necessary to maintain pregnancy.
With an anovulatory cycle, this system gets lost. Most often, the violation is associated with a change in the concentration of female hormones, which may be too much or too little. Due to hormonal imbalance, there is a significant thickening of the inner uterine layer – the endometrium.
After reaching a certain limit, the mucosa begins to peel off, which leads to a violation of the integrity of the vessels and menstrual bleeding. Its strength and duration can be different and vary from month to month. The constant thickening of the mucosa leads to the formation of polyps – mushroom-like growths, which further complicate fertilization.
In some periods of life, for example, in puberty (adolescence) and when entering menopause, this situation is considered the norm and does not require treatment. Periodic anovulatory cycles in a healthy woman are also not dangerous. Medical care is required if there is a constant absence of ovulation, which does not allow getting pregnant and negatively affects the state of health.
Causes of anovulatory cycles
- Pathologies of the pituitary gland – the cerebral process that secretes hormones that ensure the maturation of the follicle and the release of the egg. The causes of his work disorders may be brain injuries, infections or congenital underdevelopment.
- Prolactinemia is the production of prolactin, which normally should be responsible for breastfeeding, milk production and inhibit ovulation during breastfeeding. However, in some cases, the concentration of this hormonal substance increases outside the lactation period, leading to inhibition of egg development. The causes of this phenomenon are pituitary tumors, taking certain medications, cirrhosis of the liver, kidney diseases.
- Diseases of the thyroid gland, the hormones of which affect the work of all body systems. Thyroid insufficiency inhibits ovulation, and in severe cases can lead to amenorrhea – the cessation of menstruation.
- Adrenal hyperfunction. Anovulatory cycles occur with increased production of male hormones by these organs – androgens.
- Pathological processes in the ovaries that disrupt the production of female hormonal substances – estrogens. Such a condition can provoke cysts and chronic adnexitis (inflammation). Anovulatory cycles are common for polycystic ovarian disease, in which the eggs do not ovulate, but remain inside the follicles, turning into small cysts.
- An abortion performed at a late date. In this situation, the body, which has tuned in to carrying a child, gets the strongest stress. Hormonal failure occurs, leading to the shutdown of ovulation.

Symptoms of the anovulatory cycle
The complaints accompanying this violation depend on the level of hormones:
With a normal hormonal background, the absence of ovulation does not cause any complaints. According to the number of days and the volume of blood lost, the menstrual-like reaction that has occurred fits perfectly into the standard critical days. The patient learns about the problem when she decides to have a child. Conception does not occur in any way, and by contacting a doctor, the patient learns about the existing violation that led to infertility.
With increased production of female estrogen hormones – hyperestrogenism – prolonged copious menstrual discharge may occur, leading to anemia (anemia). Sometimes, due to hormonal imbalance, blood clotting decreases, which aggravates the situation.
With a decrease in the amount of female hormones – hypoestrogenia – menstruation becomes short, sparse, irregular.
Treatment anovulatory cycle
A woman is prescribed ovulation stimulation with the help of medications that affect the growth of eggs and their exit from the follicle. Medications allow you to “wake up” follicles containing eggs. The process is controlled by a gynecologist, who prescribes periodic ultrasound examinations of the ovaries, fixing the exit of germ cells into the fallopian tubes.
Against the background of the treatment, the possibility of pregnancy increases by 70%. However, artificial ovulation often knocks out several eggs from the ovaries, which increases the likelihood of multiple pregnancies.