The syndrome of age-related androgen deficiency in men is a violation of the biochemical balance that occurs in adulthood due to a lack of androgens in the blood serum, often accompanied by a decrease in the body’s sensitivity to androgens. As a rule, this leads to a significant deterioration in the quality of life and adversely affects the functions of almost all body systems. Naturally, the issues of androgen deficiency therapy are of great interest, since it poses a difficult task for a clinician: to choose from a wide arsenal of methods and drugs of hormone therapy the most optimal, combining quality, efficiency, and ease of use.
Currently, urologists and andrologists most often use testosterone replacement therapy. This method allows you to solve a number of tasks: to reduce the symptoms of age-related androgen deficiency by increasing libido, overall sexual satisfaction, to reduce the severity or completely eliminate vegetative-vascular and mental disorders. In addition, if testosterone replacement therapy is used for more than 1 year, patients experience an increase in bone density, a decrease in the severity of visceral obesity, as well as an increase in muscle mass. Also, after a long course of treatment, laboratory parameters are normalized: there is an increase in the level of hemoglobin or the number of red blood cells, a decrease in the level of VLDL (very low-density lipoproteins) and LDL (low-density lipoproteins) with an unchanged level of HDL (high-density lipoproteins). Many authors believe that such an effect can be achieved by restoring the concentration of testosterone in the blood to a normal level (10-35 nmol/l). It should also be taken into account that * 17α-alkylated testosterone preparations fluoxymesterolone and methyltestosterone have pronounced hepatotoxicity, having a toxic and carcinogenic effect on the liver, and also negatively affect the blood lipid spectrum (a sharp increase in the level of atherogenic and a decrease in the level of anti-atherogenic lipoproteins). Therefore, the use of these testosterone derivatives in clinical practice was discontinued.
Currently, testosterone undecanoate is preferred among oral medications. This testosterone ester is not subjected to primary hepatic metabolism, since it is absorbed into the lymphatic system, bypassing the liver. After the hydrolysis of testosterone undecanoate in the lymphatic system, testosterone enters the systemic bloodstream, which has a therapeutic effect both by itself and through its main metabolites-dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and estradiol, which cause the full spectrum of androgenic activity of testosterone. Thus, testosterone undecanoate retains its activity when administered orally. At the same time, bypassing the portal vein system and passing through the liver, testosterone undecanoate does not have hepatotoxic and hepatocancerogenic effects. The half-life of the drug from the plasma is 3-4 hours. In this regard, the dosage regimen of testosterone undecanoate is a 2-fold intake during the day, this is not always convenient for patients. Based on our own experience, we believe that Andriol is a fairly mild drug and helps only in cases of initial and minimal manifestations of age-related androgen deficiency.
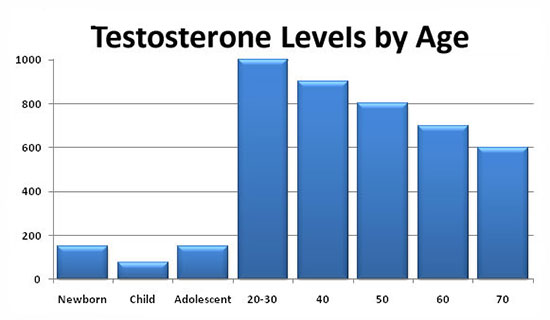
Intramuscular injections of prolonged testosterone esters are also a widely used method of substitution therapy in men with hypogonadism. The two most well – known esters of testosterone, testosterone cypionate and testosterone enanthate, have similar pharmacokinetics. With intramuscular administration of these drugs, a depot is created from which the drug is released into the bloodstream. During the first 2-3 days after administration, the testosterone level rises to supraphysiological figures, and then slowly decreases over the next 2 weeks to subnormal values. The positive side of these drugs is the duration of the therapeutic effect. Nevertheless, sharp changes in the level of testosterone, often felt by the patient himself in the form of rises and decreases in libido, general well-being, emotional status, are undesirable qualities of these drugs. In this regard, great hopes are pinned on the new drug Nebido (Sharing), the pharmacokinetics of which is significantly different from other testosterone esters. Nebido is a testosterone undecanoate and is a drug that does not have a peak increase in concentration.
Over the past two decades, much attention has been paid to the study of the benefits of transdermal use of testosterone preparations. Scrotal patches have an effective effect, and some patients consider them the most convenient method of treatment. Skin patches are most well perceived by patients and give an effective level of testosterone in the blood serum. Nevertheless, there are some differences between these two types of patches regarding their allergogenic potential: when using skin patches, there is a much higher frequency of allergic reactions and skin irritation than when using scrotal patches. Testosterone gel has all the advantages of patches and does not cause the development of skin reactions. Its only drawback is the possibility of contact of the gel with a partner and an insufficient number of long-term studies on its use.
The transdermal route of testosterone administration allows avoiding its primary metabolism in the liver and inactivation, as it happens when using oral androgenic drugs, and also allows simulating the circadian rhythms of the release of physiological unmodified testosterone and its natural metabolites, estradiol and DHT. In addition, therapy with the use of patches and gel can be easily interrupted if necessary. The positive aspects of this method of treatment also include a low risk of drug dependence.
Although the European drug 5-α-dihydrotestosterone gel (DHT) is recognized as effective, it is not known whether the isolated use of a non-aromatized androgen, such as DHT, has the same effect as testosterone, due to the fact that testosterone metabolites include estradiol. According to many authors, the use of the drug is not recommended, since DHT, due to the inability to convert into estradiol, does not have the full range of therapeutic properties of testosterone (for example, the effect on bone tissue and the cardiovascular system).
Thus, we can say that there is no optimal remedy for the treatment of age-related androgen deficiency in men. And the choice of the drug should be approached strictly individually, taking into account the patient’s age, body mass index, the need to preserve spermatogenesis, hematocrit indicators and concomitant diseases.