Clomid is a medication that is used in gynecological practice for the treatment of female infertility. It belongs to the group of antiestrogens. This means that it blocks the receptors (nerve endings) in the ovaries and hypothalamus, which leads to a decrease in the production of estrogens. Also, this drug stimulates the maturation of follicles, ovulation itself and the level of estradiol in the blood.
What are estrogens?
This is a group of steroid female sex hormones that are produced mainly in the ovaries. Men also have a small amount of estrogen in their blood, which is produced by the testicles and adrenal glands (in both sexes). Estrogens are divided into three types: estrone, estriol, and estradiol. Clomid particularly affects estradiol levels in the blood.
Functions of estrogens:
Feminization. This means that thanks to estrogens, a woman has a feminine appearance. In adolescence, these hormones are actively produced and form secondary sexual characteristics (Breasts, buttocks, abdomen, female hair growth, growth of internal and external genitals).
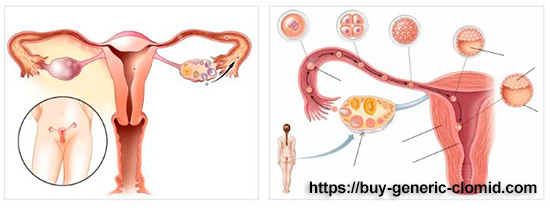
Reproduction. A group of estrogen hormones activates the production of mucus in the vagina, as well as its epithelization, which creates the necessary conditions for maintaining the viability of spermatozoa. Estrogens stimulate the maturation of the egg (follicle) and the onset of ovulation, in which the Mature egg is released from the ovary and it can be fertilized by a sperm. Further, after ovulation, in the event that fertilization occurred, estrogens are responsible for the preservation of the fetal egg, blood supply to the placenta and preparation of the expectant mother’s breast for lactation. If the egg is not fertilized by a sperm, these hormones activate the detachment of the inner layer of the uterus (endometrium) and, as a result, menstruation begins.
Other effects of estrogens include the regulation of calcium levels, cholesterol in the blood, blood pressure, liver function, and mental activity.
How Clomid works
Clomid contains the main active substance – clomiphene, which blocks the receptors that perceive estrogens in the hypothalamus (the part of the brain that controls the hormonal background of the body). As a result, the production of gonadotropins (follicle-stimulating and luteinizing) increases, which activate maturation and intra-secretory (endocrine) function of the follicle in the ovaries. As a result of all the processes described above, the use of the drug Clomid leads to the fact that the level of estradiol in the blood increases significantly.
Causes and symptoms of estrogen reduction
- The main reason that the level of estrogens in the blood of a woman decreases is the lack of activity of the ovaries that produce them. As the body ages, there is also a shortage of them. An important reason may be various pathological changes on the part of the pituitary gland.
- Sometimes there is a decrease in the level of estrogens in women who are engaged in professional sports, when the physical load on the body is excessive. This phenomenon occurs due to the fact that testosterone (the male hormone) is produced intensively.
- Another important point is the presence or absence of adipose tissue. It is proved that estrogens are also produced by fat cells. This means that exhaustion or rapid weight loss is extremely dangerous for the female body, namely for its reproductive ability.
Symptoms that occur with estrogen deficiency
- In adolescence, a lack of estrogens leads to insufficient development of secondary sexual characteristics, a decrease in the size of the uterus, late onset and failures in the menstrual cycle.
- In the reproductive age, a decrease in the level of estrogens provokes a decrease in sexual desire, sharp mood swings, various violations of the duration and other indicators of the menstrual cycle. In parallel, memory decreases, performance, insomnia appears and the skin condition worsens (its elasticity, color, turgor). Stretch marks, pigmentation, and inflammatory rashes appear on the skin. Female infertility and dysfunctional uterine bleeding may occur.
Form of release of the drug Clomid
This medicine is produced in tablet form. Each tablet contains 25mg, 50mg, 100 milligrams of clomiphene. The drug Clomid is intended for oral administration, that is, through the mouth.
Indications for use of the drug Clomid
According to the instructions for use of the drug, it is prescribed for these conditions:
- infertility caused by lack of ovulation;
- galactorrhea is a spontaneous pathological outflow of milk from the breast, which is not associated with feeding a child and occurs as a result of pituitary tumors;
- amenorrhea – absence of menstruation for a long period;
- dysfunctional uterine bleeding (metrorrhagia);
- androgen insufficiency (hypogonadism) – insufficient production of steroid hormones by the sexual glands;
- polycystic ovary;
- oligospermia in men, a condition in which the quality and activity of spermatozoa decreases;
- violation of the pituitary gland.
How to take Clomid
The scheme of application of the drug is different and depends on the pathology. As indicated in the instructions for use of the drug, to stimulate the ovulation process, Clomid is prescribed at a dose of 50 milligrams once a day, before bedtime. The course of taking the drug begins on the fifth day of the menstrual cycle and lasts five days. In situations where there is no menstruation at all, you can start taking the drug at any time prescribed by the doctor. If it is ineffective and there is no ovulation, the dose of Clomid can be increased to 150 milligrams per day, or the course of treatment can be extended to ten days. There is a special indication in the instructions, which says that the total course dose of the drug should not exceed 1 gram.
How to determine whether Clomid is effective
It is necessary to determine the presence of ovulation. To do this, there are several fairly simple methods that a woman can perform herself at home. This is a temperature method or basal temperature measurement, a method of ovulation tests. Additionally, the levels of hormones (luteinizing, progesterone, etc.) are determined.
In cases where the menstrual cycle has improved, but pregnancy does not occur, it is recommended to repeat the course of taking this drug in the same therapeutic dosage.
Contraindications to taking the drug Clomid
- Renal or hepatic insufficiency, which is associated with the way the drug is excreted.
- Neoplasm of the genitals.
- Uterine bleeding of unknown etiology.
- Inflammation of the inner layer of the uterus (endometriosis).
- A tumor or an underactive pituitary gland.
- Ovarian insufficiency on the background of increased prolactin levels in the blood.
- Ovarian cyst.
- Pregnancy.
Side effects of the drug Clomid
During the reception of Clomid, various manifestations from the internal organs may appear.
- Allergic manifestations: vasomotor disorders, allergic dermatitis, rarely-rashes.
- Manifestations from the nervous system: drowsiness, dizziness, headache, depression, insomnia, hyperexcitability, slowing down the speed of motor and mental reactions.
- Possible manifestations of the genitourinary system: an increase in the size of the ovary, cystic ovarian changes, menorrhagia, dysmenorrhea, polyuria, increased urination, pain in the lower abdomen.
- Other possible side reactions include:” flushes ” of blood to the face, alopecia (hair loss), chest pain (breast), decreased visual acuity, weight gain.
Special instructions concerning the drug Clomid
Taking this medication increases the likelihood of multiple pregnancies.
The development of effective action of the drug is possible only if the patient has a sufficient amount of their own estrogens. The lower their level, the less effective Clomid is.
Treatment with anti-estrogenic drugs, as well as any other, should take place under the careful supervision of a gynecologist. Periodically, the ovarian function is determined and other special examinations, including vaginal ones, are performed.
During the course of therapeutic treatment with Clomid, it is recommended to take special care when working with mechanisms that carry a potential danger, and when driving a car.