Today we publish the continuation of the article “Signs and symptoms of ovulation, feelings of a woman”, the first part can be read here
The feeling after ovulation
Some women, especially those who use the calendar method of pregnancy prevention, are interested in symptoms after ovulation. This is how women calculate “safe” days for unwanted pregnancies. These signs are very unusual and may coincide with the early symptoms of pregnancy:
Vaginal discharge
As soon as the egg is released from the main follicle and dies (its life span is 24, maximum 48 hours), the discharge from the genital tract also changes. Vaginal whites lose their transparency, become milky, possibly interspersed with small lumps, sticky and poorly drawn.
Pains
Within one to two days after ovulation, discomfort and minor pain in the lower abdomen disappear.
Libido
Gradually, sexual desire also fades, since now it makes no sense for spermatozoa to meet with an egg, it has already died.
Basal temperature
If the basal temperature is significantly higher than 37 degrees at the moment of rupture of the Graaf vesicle, then after ovulation it decreases by several tenths of a degree, although it remains above the 37 degree mark. This sign is unreliable, since even with conception, the basal temperature will be above the 37-degree mark. The only difference is that by the end of the second phase (before the start of menstruation), the temperature will drop to 37 degrees or lower.
Acne
On the eve and at the time of ovulation, hormonal changes occur in the body, which affects the condition of the skin of the face – acne appears. Once ovulation is complete, the rash gradually disappears.
Ultrasound data
Ultrasound allows you to identify the dominant follicle that has fallen due to the rupture, a small amount of fluid in the post-uterine space, and later the yellow body that is forming. Ultrasound data are most significant in the case of dynamic research (maturation of follicles, determination of the dominant follicle and its subsequent rupture).
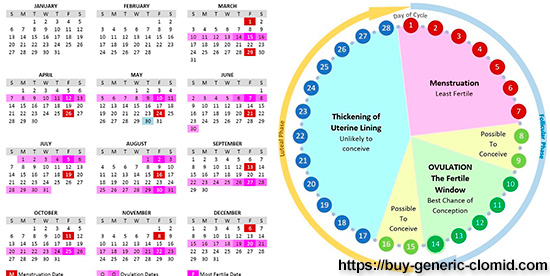
Calendar method for determining ovulation
Ovulation is the release of a Mature egg from the ovary. The egg Matures during the menstrual cycle, which is necessary for the preparation of the uterus and the maturation of the egg, the result of which is ovulation. To determine ovulation using the calendar method, you need to know your menstrual cycle for the last few months. Knowing the cycle, you can calculate its length, i.e. the period from the beginning of one month to the beginning of the next. From the total duration of the cycle, 14 days are subtracted. So, if the cycle is 28 days, then subtracting 14 days, we get the 14th day of the cycle, in which the egg can be released from the ovary. For conception during the week before and after ovulation, the couple is recommended to have an active sexual life, preferably with breaks of 1-2 days, in order to have time to Mature the sperm. As already calculated above, the release of a Mature egg occurs somewhere in the middle of the menstrual cycle.
However, every woman may have ovulation shifts a few days later, this may be due to infectious pathologies of the reproductive system; excessive physical exertion; stress and hormonal disorders.
Among the causes of early ovulation, the following can be distinguished: disorders in the balance of estrogen and progesterone hormone; disorders in the adrenal cortex; colds and flu diseases, etc. Such factors may well trigger the onset of early ovulation. In addition, each cause can affect other systems of the female body. Therefore, to avoid this, it is recommended to avoid such factors that may affect ovulation and, as a result, the bearing of a child in the future. Premature ovulation is dangerous if it repeatedly occurs in the female body, in this case, the reasons lie in hormonal failures and other various abnormalities, a woman may need gynecological intervention. In addition, it is possible that pregnancy will not occur for a long time, if only the couple focuses on the middle of the cycle. Or, on the contrary, the onset of an unwanted pregnancy, if the woman is not protected at the beginning of the cycle, again using the calendar method. Over the course of a woman’s life, ovulatory shifts in different directions are periodically observed, so there may be a late release of the egg.
The reasons for late ovulation lie in the following: hormonal disorders in the body; lack of weight, because lack of adipose tissue negatively affects the production of estrogen, provoking a delay in maturation and exit of the female cell; taking emergency contraceptives in the past; gynecological pathologies, infections and lack of menstruation, are also characteristic companions of late egg release. To restore the cycle, a woman needs to undergo a full examination, after which appropriate treatment is prescribed.
After accurate compliance with all medical recommendations, ovulatory processes are normalized, the cycle is restored and a long-awaited pregnancy occurs.
Determination of ovulation by basal body temperature
Basal temperature measurements are performed in the morning, however, it is not advisable to get out of bed before measuring, so prepare a thermometer in the evening. To measure the temperature, you can use both a simple mercury thermometer and an electronic one. Carefully insert the thermometer into the rectum and hold it there for five to seven minutes. Record the measured temperature in the table every day, except for days when a woman has her period. After taking measurements throughout the cycle, you need to build a graph. To build a table, you can specify the days of temperature measurement on the top, and on the left, specify the possible BTT on these days. At the junction of the lines, put points that are connected by a straight line.
On days when there is a sharp increase in body temperature, after its rapid decrease, and ovulation occurs. This jump is explained by the fact that during ovulation, the hormone progesterone is actively produced, which affects the thermoregulation center in the brain. It is its increase that leads to fluctuations in BTT, which increases sharply after the release of a Mature egg. If you notice strong, atypical changes in temperature, or it does not change at all, you need to see a doctor to find the cause, which may be due to estrogen deficiency or other factors. It is easy to create a basal temperature chart using special applications that are placed on some women’s websites or in applications.
This method is available, but not 100% reliable, because there is not always time to measure the temperature, you can also just forget about the measurement, missed days can significantly change the picture and schedule of building the BTT
In addition, factors such as medication, sexual intercourse, climate change, stress, etc. can affect the usual and normal schedule for building BTT. Therefore, for greater confidence in determining day X, an ovulation test that is sold at any pharmacy can help.
My period comes on 14 in the past two months,and I want to conceive a baby boy how will I count it
https://always.com/en-us/period-calculator